
Governors, Governor Generals, and Viceroys in British India
This is a comprehensive study resource designed for competitive exam aspirants, focusing on the colonial administration of British India. It provides detailed notes in both English and Malayalam covering the key Governors, Governor Generals, and Viceroys from 1757 to 1950.
The notes detail the tenure, major reforms (such as the Permanent Settlement, Subsidiary Alliance, and administrative changes), significant acts, and pivotal historical events associated with each administrator, from Robert Clive to C. Rajagopalachari. A visual timeline image is also included to summarize the chronological order of these rulers.

I. Governors of Bengal (1757–1773)
Robert Clive (1757–60, 1765–67)

- First Governor of Bengal.
- Introduced the Dual Government System in Bengal (1765).
- Signed the Treaty of Allahabad (1765) following the Battle of Buxar.
II. Governor Generals of Bengal (1773–1833)
Warren Hastings (1773–1785)
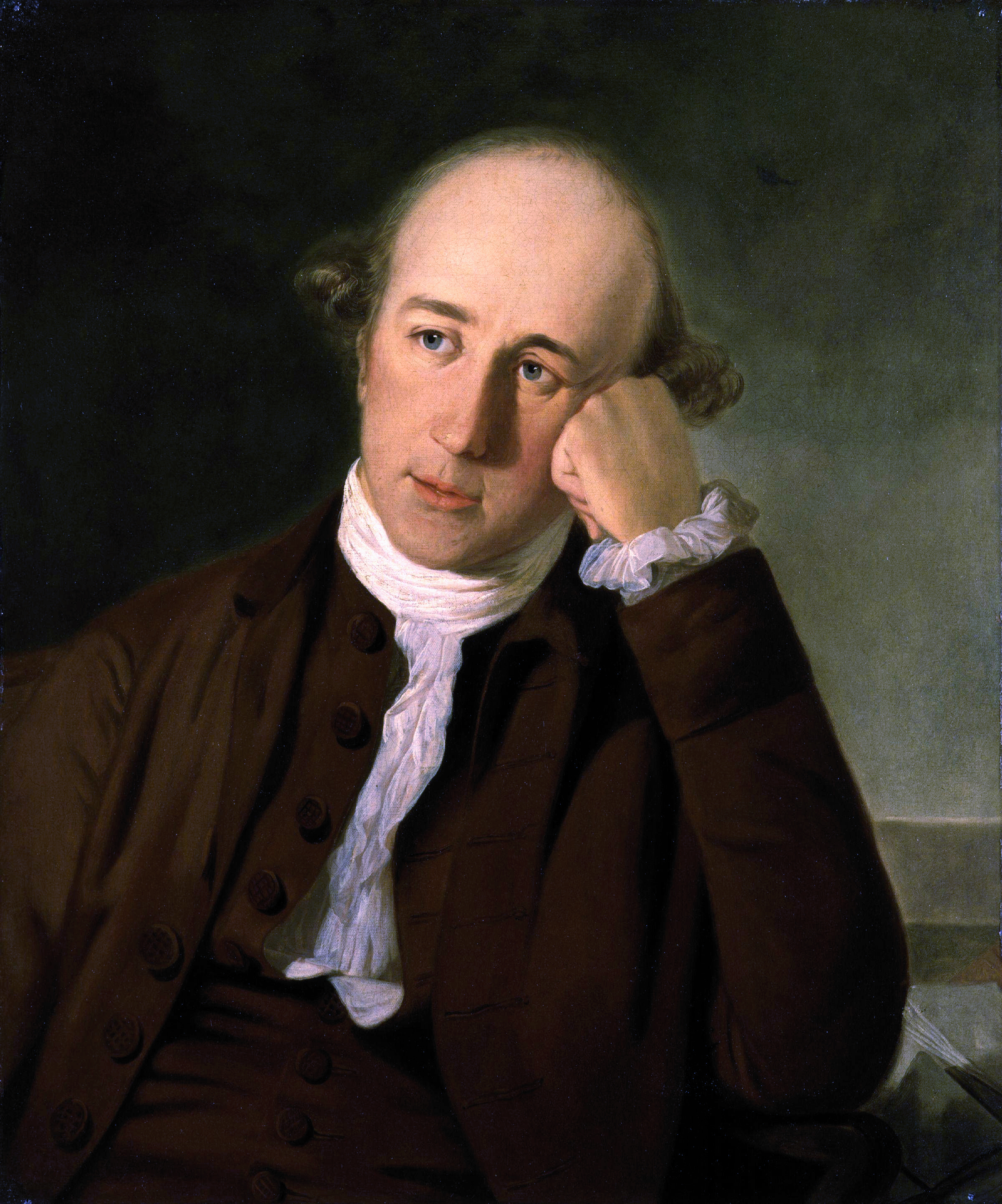
- First Governor General of Bengal (appointed under the Regulating Act of 1773).
- Abolished the Dual Government System.
- Founded the Asiatic Society of Bengal with William Jones in 1784.
- Established the first Supreme Court in Calcutta.
- The only Governor General to be impeached by the British Parliament.
Lord Cornwallis (1786–1793)

- Known as the Father of Indian Civil Services.
- Introduced the Permanent Settlement (Zamindari System) in Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha in 1793.
- Introduced the Cornwallis Code.
- Established lower courts and appellate courts.
Lord Wellesley (1798–1805)

- Introduced the Subsidiary Alliance System (1798). The Nizam of Hyderabad was the first ruler to sign it.
- Described himself as the 'Bengal Tiger'.
- Established Fort William College in Calcutta for training civil servants.
III. Governor Generals of India (1833–1858)
Lord William Bentinck (1828–1835)

- First Governor General of India (designated by the Charter Act of 1833).
- Abolished Sati in 1829 (with the support of Raja Ram Mohan Roy).
- Suppressed the 'Thugs' (robber gangs).
- Introduced English as the medium of higher education (based on Macaulay’s Minute, 1835).
Lord Dalhousie (1848–1856)

- Introduced the Doctrine of Lapse. Satara was the first state annexed under this policy.
- Known as the Father of Indian Railways (First railway line: Bombay to Thane, 1853).
- Started the first telegraph line and introduced the modern postal system.
- Established the Public Works Department (PWD).
- Drafted the Widow Remarriage Act (passed in 1856).
IV. Viceroys of India (1858–1947)
Lord Canning (1856–1862)

- First Viceroy of India (appointed after the Government of India Act 1858).
- Viceroy during the Revolt of 1857.
- Withdrew the Doctrine of Lapse.
- Introduced the Budget system and Income Tax in India.
- Established High Courts in Calcutta, Bombay, and Madras (1862).
Lord Mayo (1869–1872)

- Organized the first Census in India (1872).
- Established Mayo College in Ajmer.
- The only Viceroy to be murdered in office (assassinated by Sher Ali Afridi in the Andaman Islands).
Lord Lytton (1876–1880)

- Passed the Vernacular Press Act (1878) (also known as the Gagging Act).
- Passed the Arms Act (1878).
- Organized the Grand Delhi Durbar in 1877 to proclaim Queen Victoria as the Empress of India.
Lord Ripon (1880–1884)

- Known as the Father of Local Self-Government in India.
- Repealed the Vernacular Press Act (1882).
- Appointed the Hunter Commission (1882) for educational reforms.
- Introduced the Ilbert Bill (allowed Indian judges to try Europeans).
- Conducted the first official/regular Census in 1881.
Lord Curzon (1899–1905)

- Responsible for the Partition of Bengal (1905).
- Passed the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act (1904).
- Established the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- Appointed the Raleigh Commission (Universities Commission).
Lord Minto II (1905–1910)

- Introduced the Minto-Morley Reforms (1909) (Indian Councils Act 1909).
- Introduced the system of communal electorates (separate electorates for Muslims).
- Surat Split of Congress (1907) occurred during his tenure.
Lord Chelmsford (1916–1921)

- Associated with the Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms (1919).
- Jallianwala Bagh Massacre (1919) took place during his tenure.
- Passed the Rowlatt Act (1919).
- Non-Cooperation Movement started.
Lord Irwin (1926–1931)

- Simon Commission visited India (1928).
- Gandhi-Irwin Pact was signed (1931).
- First Round Table Conference held in London.
- Dandi March and Civil Disobedience Movement launched.
Lord Linlithgow (1936–1944)

- Longest serving Viceroy of India.
- Quit India Movement (1942) occurred during his tenure.
- Proposed the August Offer (1940).
- Cripps Mission visited India (1942).
Lord Mountbatten (1947)

- Last Viceroy of British India and the First Governor General of Independent India.
- Proposed the 'Mountbatten Plan' (June 3 Plan) for the partition and independence of India.
C. Rajagopalachari (1948–1950)
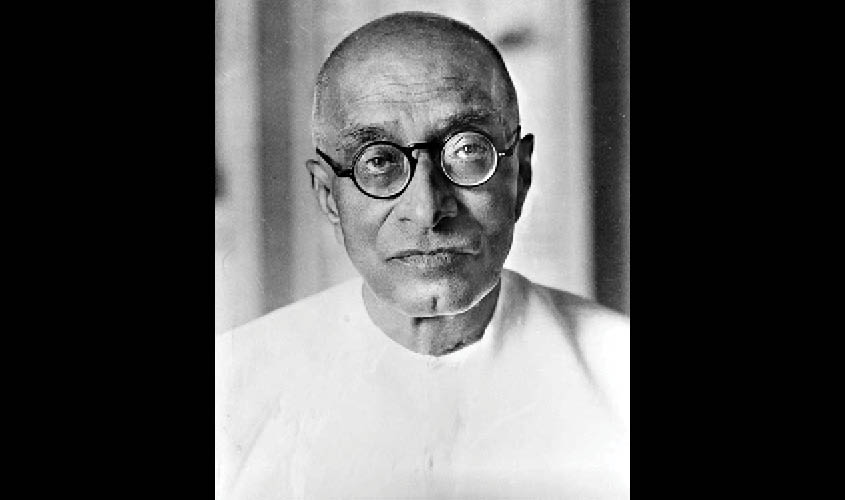

- First and last Indian Governor General of Independent India.
ബ്രിട്ടീഷ് ഇന്ത്യയിലെ ഗവർണർമാർ, ഗവർണർ ജനറൽമാർ, വൈസ്രോയിമാർ
I. ബംഗാൾ ഗവർണർമാർ (1757–1773)
റോബർട്ട് ക്ലൈവ് (1757–60, 1765–67)
- ബംഗാളിലെ ആദ്യത്തെ ഗവർണർ.
- ബംഗാളിൽ ദ്വിഭരണ സംവിധാനം (Dual Government) ഏർപ്പെടുത്തി (1765).
- ബക്സാർ യുദ്ധത്തിന് ശേഷം 1765-ൽ അലഹബാദ് സന്ധിയിൽ ഒപ്പുവെച്ചു.
II. ബംഗാൾ ഗവർണർ ജനറൽമാർ (1773–1833)
വാറൻ ഹേസ്റ്റിംഗ്സ് (1773–1785)
- ബംഗാളിലെ ആദ്യത്തെ ഗവർണർ ജനറൽ (1773 ലെ റെഗുലേറ്റിംഗ് ആക്ട് പ്രകാരം).
- ദ്വിഭരണ സംവിധാനം (Dual Government) നിർത്തലാക്കി.
- 1784-ൽ വില്യം ജോൺസിനൊപ്പം ചേർന്ന് ഏഷ്യാറ്റിക് സൊസൈറ്റി ഓഫ് ബംഗാൾ സ്ഥാപിച്ചു.
- കൽക്കട്ടയിൽ സുപ്രീം കോടതി സ്ഥാപിച്ചു.
- ബ്രിട്ടീഷ് പാർലമെന്റ് ഇംപീച്ച് (കുറ്റവിചാരണ) ചെയ്ത ഏക ഗവർണർ ജനറൽ.
ലോർഡ് കോൺവാലിസ് (1786–1793)
- ഇന്ത്യൻ സിവിൽ സർവീസിന്റെ പിതാവ് എന്നറിയപ്പെടുന്നു.
- 1793-ൽ ബംഗാൾ, ബീഹാർ, ഒഡീഷ എന്നിവിടങ്ങളിൽ സ്ഥിര നികുതി വ്യവസ്ഥ (Permanent Settlement / Zamindari System) നടപ്പിലാക്കി.
- കോൺവാലിസ് കോഡ് അവതരിപ്പിച്ചു.
- താഴ്ന്ന കോടതികളും അപ്പീൽ കോടതികളും സ്ഥാപിച്ചു.
ലോർഡ് വെല്ലസ്ലി (1798–1805)
- സൈനിക സഹായ വ്യവസ്ഥ (Subsidiary Alliance) നടപ്പിലാക്കി (1798). ഹൈദരാബാദ് നിസാം ആണ് ഇതിൽ ആദ്യം ഒപ്പുവെച്ചത്.
- സ്വയം 'ബംഗാൾ കടുവ' എന്ന് വിശേഷിപ്പിച്ചു.
- സിവിൽ സർവീസുകാർക്ക് പരിശീലനം നൽകാനായി ഫോർട്ട് വില്യം കോളേജ് സ്ഥാപിച്ചു.
III. ഇന്ത്യൻ ഗവർണർ ജനറൽമാർ (1833–1858)
ലോർഡ് വില്യം ബെന്റിക് (1828–1835)
- ഇന്ത്യയിലെ ആദ്യത്തെ ഗവർണർ ജനറൽ (1833 ലെ ചാർട്ടർ ആക്ട് പ്രകാരം).
- 1829-ൽ സതി നിർത്തലാക്കി (രാജാ റാം മോഹൻ റോയിയുടെ സഹായത്തോടെ).
- തഗ്ഗുകൾ എന്നറിയപ്പെട്ടിരുന്ന കൊള്ളസംഘത്തെ അടിച്ചമർത്തി.
- ഉന്നത വിദ്യാഭ്യാസ മാധ്യമമായി ഇംഗ്ലീഷിനെ മാറ്റി (മക്കാളെ മിനിറ്റ്സ്, 1835).
ലോർഡ് ഡൽഹൗസി (1848–1856)
- ദത്തവകാശ നിരോധന നിയമം (Doctrine of Lapse) കൊണ്ടുവന്നു. സത്താറയാണ് ഈ നിയമപ്രകാരം പിടിച്ചെടുത്ത ആദ്യ രാജ്യം.
- ഇന്ത്യൻ റെയിൽവേയുടെ പിതാവ് (ആദ്യത്തെ റെയിൽവേ പാത: ബോംബെ മുതൽ താനെ വരെ, 1853).
- ആദ്യത്തെ ടെലിഗ്രാഫ് ലൈൻ ആരംഭിച്ചു, ആധുനിക തപാൽ സംവിധാനം കൊണ്ടുവന്നു.
- പൊതുമരാമത്ത് വകുപ്പ് (PWD) സ്ഥാപിച്ചു.
- വിധവാ പുനർവിവാഹ നിയമത്തിന്റെ കരട് തയ്യാറാക്കി (1856-ൽ പാസാക്കി).
IV. ഇന്ത്യൻ വൈസ്രോയിമാർ (1858–1947)
ലോർഡ് കാനിംഗ് (1856–1862)
- ഇന്ത്യയിലെ ആദ്യത്തെ വൈസ്രോയി (1858 ലെ ഗവൺമെന്റ് ഓഫ് ഇന്ത്യ ആക്ട് പ്രകാരം).
- 1857 ലെ വിപ്ലവ സമയത്തെ വൈസ്രോയി.
- ദത്തവകാശ നിരോധന നിയമം പിൻവലിച്ചു.
- ഇന്ത്യയിൽ ബജറ്റ് സമ്പ്രദായവും ആദായ നികുതിയും അവതരിപ്പിച്ചു.
- 1862-ൽ കൽക്കട്ട, ബോംബെ, മദ്രാസ് എന്നിവിടങ്ങളിൽ ഹൈക്കോടതികൾ സ്ഥാപിച്ചു.
ലോർഡ് മേയോ (1869–1872)
- ഇന്ത്യയിൽ ആദ്യമായി സെൻസസ് എടുത്തു (1872).
- അജ്മീറിൽ മേയോ കോളേജ് സ്ഥാപിച്ചു.
- ഔദ്യോഗിക പദവിയിലിരിക്കെ കൊല്ലപ്പെട്ട ഏക വൈസ്രോയി (ആൻഡമാൻ ദ്വീപുകളിൽ വെച്ച് ഷേർ അലി അഫ്രീദി കൊലപ്പെടുത്തി).
ലോർഡ് ലിറ്റൺ (1876–1880)
- പ്രാദേശിക ഭാഷാ പത്ര നിയമം (Vernacular Press Act) (1878) പാസാക്കി.
- ആയുധ നിയമം (Arms Act) (1878) പാസാക്കി.
- 1877-ൽ ഡൽഹി ദർബാർ സംഘടിപ്പിച്ചു (വിക്ടോറിയ രാജ്ഞിയെ ഇന്ത്യയുടെ ചക്രവർത്തിനിയായി പ്രഖ്യാപിച്ചു).
ലോർഡ് റിപ്പൺ (1880–1884)
- ഇന്ത്യയിലെ തദ്ദേശ സ്വയംഭരണത്തിന്റെ പിതാവ്.
- പ്രാദേശിക ഭാഷാ പത്ര നിയമം പിൻവലിച്ചു (1882).
- വിദ്യാഭ്യാസ പരിഷ്കാരങ്ങൾക്കായി ഹണ്ടർ കമ്മീഷനെ (1882) നിയമിച്ചു.
- ഇൽബർട്ട് ബിൽ അവതരിപ്പിച്ചു (ഇന്ത്യൻ ജഡ്ജിമാർക്ക് യൂറോപ്യന്മാരെ വിചാരണ ചെയ്യാൻ അധികാരം നൽകി).
- 1881-ൽ ആദ്യത്തെ ഔദ്യോഗിക സെൻസസ് നടത്തി.
ലോർഡ് കഴ്സൺ (1899–1905)
- ബംഗാൾ വിഭജനം (1905) നടപ്പിലാക്കി.
- പുരാതന സ്മാരക സംരക്ഷണ നിയമം (1904) പാസാക്കി.
- ആർക്കിയോളജിക്കൽ സർവേ ഓഫ് ഇന്ത്യ (ASI) സ്ഥാപിച്ചു.
- റാലേ കമ്മീഷൻ (സർവ്വകലാശാല കമ്മീഷൻ) നിയമിച്ചു.
ലോർഡ് മിന്റോ II (1905–1910)
- മിന്റോ-മോർലി പരിഷ്കാരങ്ങൾ (1909) (ഇന്ത്യൻ കൗൺസിൽ ആക്ട് 1909) നടപ്പിലാക്കി.
- മുസ്ലീങ്ങൾക്ക് പ്രത്യേക നിയോജകമണ്ഡലങ്ങൾ (Separate electorates) അനുവദിച്ചു.
- കോൺഗ്രസിലെ സൂററ്റ് പിളർപ്പ് (1907) ഇദ്ദേഹത്തിന്റെ കാലത്താണ് നടന്നത്.
ലോർഡ് ചെംസ്ഫോർഡ് (1916–1921)
- മോണ്ടാഗു-ചെംസ്ഫോർഡ് പരിഷ്കാരങ്ങൾ (1919).
- ജാലിയൻ വാലാബാഗ് കൂട്ടക്കൊല (1919) ഇദ്ദേഹത്തിന്റെ കാലത്താണ് നടന്നത്.
- റൗലറ്റ് ആക്ട് (1919) പാസാക്കി.
- നിസ്സഹകരണ പ്രസ്ഥാനം ആരംഭിച്ചു.
ലോർഡ് ഇർവിൻ (1926–1931)
- സൈമൺ കമ്മീഷൻ ഇന്ത്യ സന്ദർശിച്ചു (1928).
- ഗാന്ധി-ഇർവിൻ ഉടമ്പടി ഒപ്പുവെച്ചു (1931).
- ലണ്ടനിൽ ഒന്നാം വട്ടമേശ സമ്മേളനം നടന്നു.
- ദണ്ഡി യാത്രയും സിവിൽ നിയമലംഘന പ്രസ്ഥാനവും നടന്നു.
ലോർഡ് ലിൻലിത്ഗോ (1936–1944)
- ഏറ്റവും കൂടുതൽ കാലം വൈസ്രോയി ആയിരുന്ന വ്യക്തി.
- ക്വിറ്റ് ഇന്ത്യ സമരം (1942) ഇദ്ദേഹത്തിന്റെ കാലത്താണ് നടന്നത്.
- ഓഗസ്റ്റ് ഓഫർ (1940) നിർദ്ദേശിച്ചു.
- ക്രിപ്സ് മിഷൻ ഇന്ത്യ സന്ദർശിച്ചു (1942).
ലോർഡ് മൗണ്ട് ബാറ്റൺ (1947)
- ബ്രിട്ടീഷ് ഇന്ത്യയിലെ അവസാനത്തെ വൈസ്രോയിയും സ്വതന്ത്ര ഇന്ത്യയിലെ ആദ്യത്തെ ഗവർണർ ജനറലും.
- ഇന്ത്യ വിഭജനത്തിനും സ്വാതന്ത്ര്യത്തിനുമായി 'മൗണ്ട് ബാറ്റൺ പ്ലാൻ' (ജൂൺ 3 പ്ലാൻ) അവതരിപ്പിച്ചു.
സി. രാജഗോപാലാചാരി (1948–1950)
- സ്വതന്ത്ര ഇന്ത്യയിലെ ആദ്യത്തെയും അവസാനത്തെയും ഇന്ത്യൻ ഗവർണർ ജനറൽ.
